Step into the world of healthcare for aging populations, where specialized programs and technological advancements play a crucial role in enhancing the well-being of the elderly. From tailored healthcare initiatives to the transformative impact of technology, this topic delves into the intricacies of providing quality care for older individuals.
Healthcare for Aging Populations
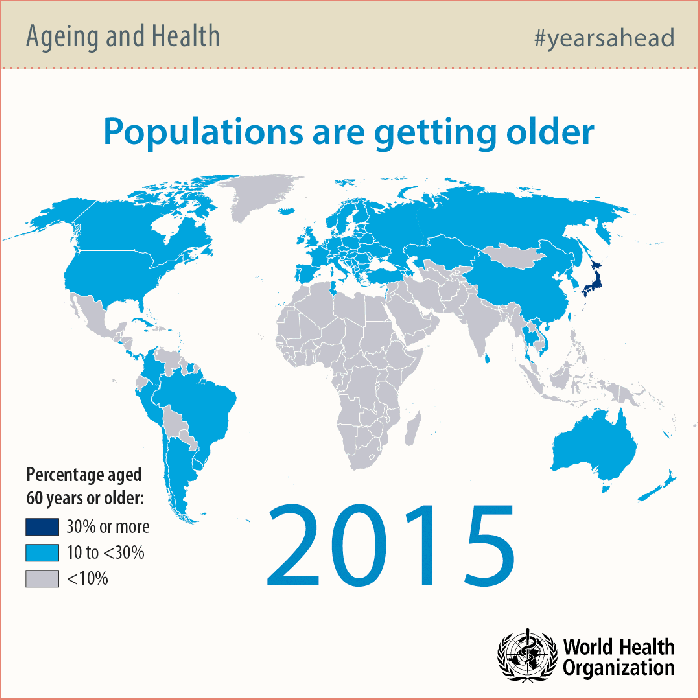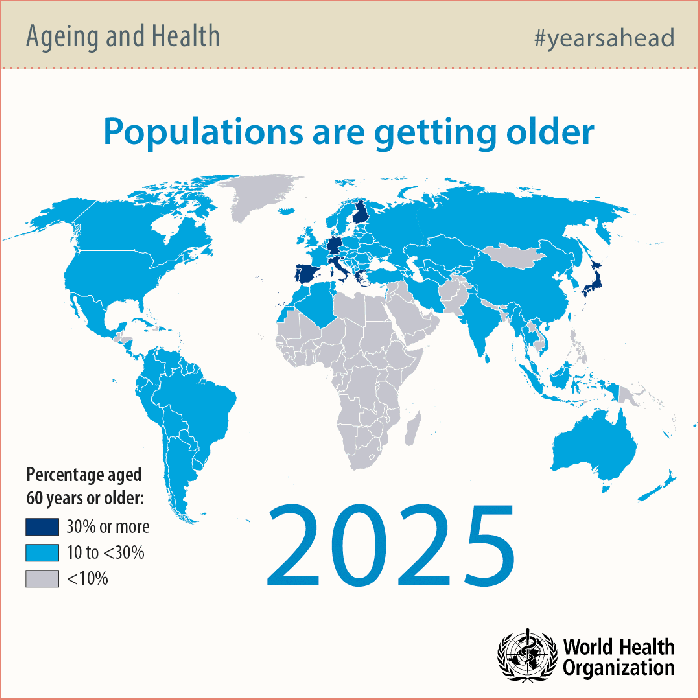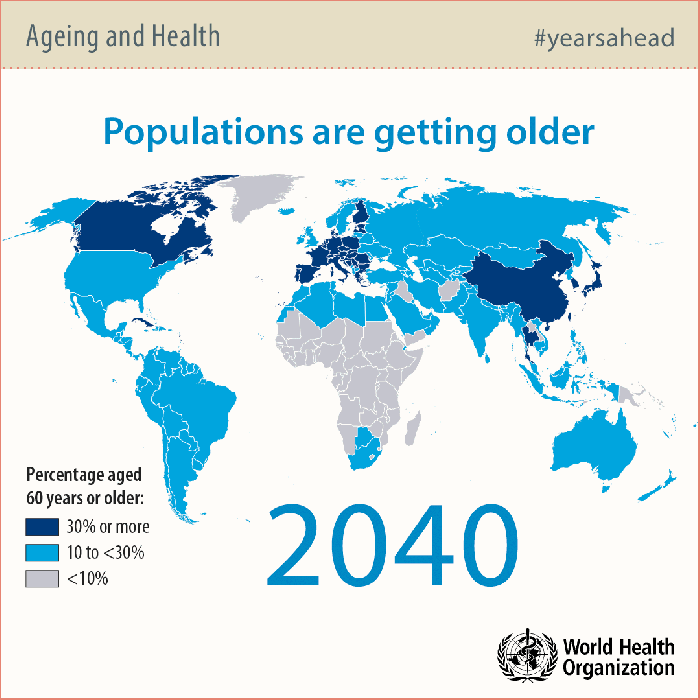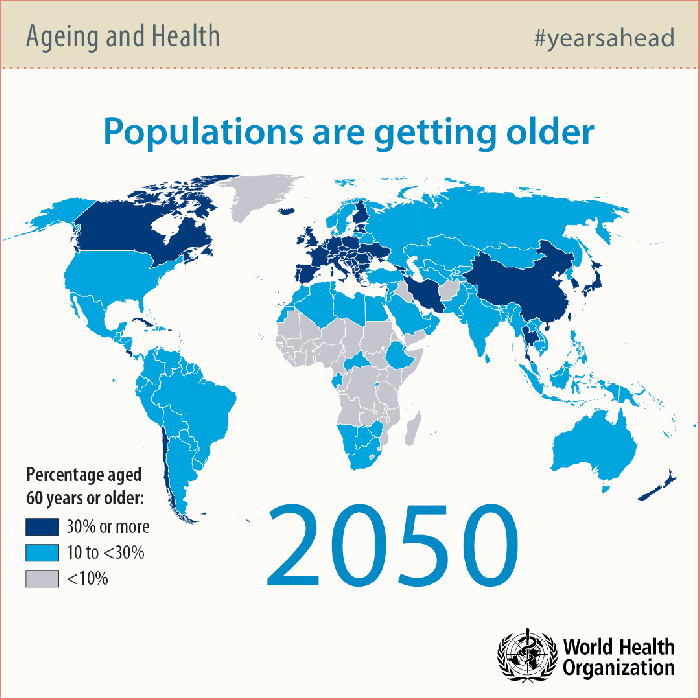
As the population continues to age, specialized healthcare for the elderly becomes increasingly important to ensure their well-being and quality of life. This tailored approach addresses the unique healthcare needs of aging individuals, considering factors such as chronic conditions, mobility issues, and cognitive decline.
Common Health Issues Faced by Aging Populations
- Cardiovascular diseases: Elderly individuals are at higher risk of heart-related conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
- Osteoporosis: Aging leads to bone loss, making seniors more susceptible to fractures and osteoporosis.
- Dementia: Cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s disease are common in the elderly population.
- Falls: Reduced balance and mobility increase the risk of falls, leading to injuries and hospitalizations.
Healthcare Programs Tailored for the Elderly
- Geriatric Care Management: Coordinating healthcare services, managing medications, and providing support for elderly patients.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on improving quality of life for elderly patients with serious illnesses, offering pain management and emotional support.
- Fall Prevention Programs: Targeting interventions to reduce fall risks through exercise, home modifications, and education.
Impact of Technology on Improving Healthcare for Aging Populations
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing healthcare for the elderly, offering innovative solutions to address their unique needs.
Telemedicine allows seniors to consult with healthcare providers remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving access to care.
Wearable devices can monitor vital signs and activity levels, providing valuable data for early detection of health issues.
Electronic health records streamline communication between healthcare providers and ensure comprehensive care coordination for elderly patients.
Health Addictions
Addiction in the elderly population poses unique challenges due to factors such as age-related physical changes, loneliness, and coexisting health conditions. Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in identifying and addressing addiction issues in aging populations to improve their overall well-being.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and social workers, play a vital role in recognizing and addressing addiction issues in older adults. They can provide comprehensive assessments, offer counseling and support services, and collaborate with other healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans.
- Educating older adults about the risks of addiction and the importance of seeking help.
- Screening for substance abuse during routine medical visits and addressing any concerns promptly.
- Collaborating with addiction specialists to develop tailored treatment plans that consider the individual needs of older adults.
- Providing ongoing support and monitoring to ensure successful recovery and prevent relapse.
Integration of Addiction Treatment in Geriatric Care
Integrating addiction treatment into geriatric care requires a multidisciplinary approach that considers the unique needs of older adults. This can involve incorporating addiction specialists into geriatric healthcare teams, providing training to healthcare professionals on addiction issues in aging populations, and implementing screening protocols for early detection of substance abuse.
- Developing specialized addiction treatment programs for older adults that address their physical, mental, and social needs.
- Offering support groups and counseling services specifically tailored to the challenges faced by older adults with addiction.
- Implementing medication management strategies to address addiction issues while considering age-related changes in metabolism and medication interactions.
Successful Addiction Treatment Programs for the Elderly
There are several successful addiction treatment programs designed specifically for older adults, such as:
- The Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation’s Older Adult Program, which provides specialized addiction treatment for individuals aged 55 and older.
- The SMART Recovery for Older Adults program, which offers support groups and resources tailored to the needs of older adults recovering from addiction.
- The Older Adult Substance Abuse and Mental Health Program at McLean Hospital, which provides comprehensive treatment for older adults with co-occurring addiction and mental health disorders.
Alternative Treatment
Alternative treatments in geriatric care refer to non-traditional or complementary therapies that are used in conjunction with or as an alternative to conventional medical interventions.
Benefits and Risks of Alternative Treatment Options
Alternative treatments offer a holistic approach to healthcare, focusing on the mind, body, and spirit. They can help alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and promote overall well-being in aging populations. However, it is essential to consider the potential risks and limitations of these therapies, as they may not always have scientific evidence to support their effectiveness.
- Benefits:
- Reduced side effects compared to conventional medications
- Promotion of relaxation and stress reduction
- Enhanced emotional and spiritual well-being
- Risks:
- Lack of regulation and standardization
- Potential interactions with prescribed medications
- Financial costs without guaranteed results
Examples of Alternative Therapies
Some alternative therapies have shown promising results in elderly patients, complementing their conventional medical treatments:
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and improve overall health.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to enhance flexibility, balance, and mental well-being.
- Massage therapy: Massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation in elderly individuals.
Comparison with Traditional Healthcare Approaches
While traditional healthcare approaches focus primarily on treating specific medical conditions with medications or procedures, alternative treatments take a more holistic approach, addressing the individual’s physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. By combining both traditional and alternative therapies, healthcare providers can offer comprehensive care tailored to the unique needs of aging populations.
Health Dentistry
As individuals age, dental care becomes increasingly important for maintaining overall health and well-being. Proper oral hygiene can prevent a myriad of dental issues and contribute to better quality of life in older adults.
Common dental issues faced by aging populations include:
Tooth Decay and Cavities
- Tooth decay and cavities can become more prevalent in older adults due to a combination of factors such as decreased saliva production, changes in diet, and medications that may affect oral health.
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential to detect and treat cavities early on.
Gum Disease
- Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, can lead to serious oral health complications if left untreated.
- Age-related changes in the gums, such as receding gums and bone loss, can make older adults more susceptible to gum disease.
Tooth Loss
- Tooth loss is a common issue among the elderly, often caused by untreated cavities, gum disease, or other oral health problems.
- Missing teeth can impact chewing ability, speech, and self-confidence, highlighting the importance of replacing missing teeth with dentures or dental implants.
Age-related changes can significantly impact oral health in the elderly:
- Decreased saliva production can lead to dry mouth, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Changes in taste buds may affect appetite and proper nutrition.
- Reduced dexterity and mobility may make it challenging for older adults to brush and floss effectively.
To maintain good oral hygiene in older adults, it is essential to:
- Brush teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce bacteria in the mouth.
- Stay hydrated and chew sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva production.
- Visit the dentist regularly for check-ups, cleanings, and treatment of any dental issues.
Health Fitness
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in promoting healthy aging by improving overall physical and mental well-being. It helps maintain muscle strength, flexibility, balance, and cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases and enhancing quality of life for the elderly.
Significance of Physical Activity for Healthy Aging
- Engaging in regular exercise can help seniors maintain independence and mobility as they age.
- Physical activity can also improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of conditions like dementia.
- Exercise boosts mood and helps alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety often experienced in older adults.
Exercise Recommendations for Elderly Individuals
- Seniors should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days.
- Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are ideal for older adults to reduce the risk of injury.
- Flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, are essential for maintaining mobility and preventing falls.
Fitness Programs for Aging Populations
- SilverSneakers: A fitness program designed specifically for seniors, offering a variety of classes focused on strength, flexibility, and balance training.
- Aqua aerobics: Water-based exercises provide a low-impact workout that is gentle on the joints, making it ideal for older adults.
- Chair yoga: A modified yoga practice that can be done while seated, helping seniors improve flexibility and reduce stress.
Role of Physical Therapy in Promoting Health and Mobility
- Physical therapy plays a vital role in helping elderly individuals recover from injuries, surgeries, or manage chronic conditions.
- Therapists work with seniors to improve strength, balance, and mobility through tailored exercise programs and techniques.
- Physical therapy can also help alleviate pain and improve overall quality of life for older adults.
Health Medicine
Medication management in aging populations poses unique challenges due to factors such as multiple chronic conditions, cognitive decline, and polypharmacy. It is essential to address these challenges effectively to ensure the well-being of elderly patients.
Common Medication-Related Issues Faced by the Elderly
- Polypharmacy: Elderly individuals often take multiple medications for various health conditions, increasing the risk of drug interactions and adverse effects.
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Aging bodies may react differently to medications, leading to side effects that can impact the overall health and quality of life.
- Medication Non-Adherence: Forgetfulness, complex dosing schedules, and cost issues can contribute to older adults not taking their medications as prescribed.
Strategies for Optimizing Medication Use in Older Adults
- Medication Reconciliation: Regularly review all medications with healthcare providers to ensure appropriateness and minimize duplication.
- Simplify Regimens: Consolidate medications when possible, use pill organizers, and set reminders to enhance adherence.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of medication effectiveness and side effects, adjusting dosages as needed under medical supervision.
Specialized Medication Regimens for Elderly Patients
- Anticoagulant Therapy: Elderly individuals requiring blood thinners may need dosage adjustments based on age-related changes in metabolism and kidney function.
- Pain Management: Older adults with chronic pain may benefit from alternative medications or lower doses to minimize side effects and interactions.
- Antidepressant Treatment: Considerations such as drug interactions and potential cognitive effects are crucial when prescribing antidepressants to the elderly.
Health Pharmacy
Pharmaceutical care plays a crucial role in the well-being of aging populations, ensuring safe and effective medication management to promote overall health and quality of life.
Importance of Pharmaceutical Care for Aging Populations
- Pharmacists provide personalized medication management strategies tailored to the specific needs of geriatric patients, taking into account factors such as multiple chronic conditions, polypharmacy, and age-related changes in metabolism.
- Through medication therapy management, pharmacists collaborate with healthcare providers to optimize drug therapy, reduce adverse drug reactions, and improve treatment outcomes for the elderly.
- Pharmaceutical care helps prevent medication errors, enhance medication adherence, and minimize drug interactions, ultimately contributing to the overall health and well-being of older adults.
Role of Pharmacists in Promoting Medication Safety and Adherence
- Pharmacists educate geriatric patients about their medications, including proper usage, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to prescribed regimens.
- Pharmacists conduct medication reviews to identify and resolve any discrepancies, ensuring that older adults receive appropriate and safe drug therapy.
- Pharmacists collaborate with healthcare teams to develop comprehensive medication plans that address the unique needs and challenges faced by aging individuals.
Examples of Pharmacy Services for Geriatric Patients
- Medication synchronization programs to simplify medication refills and reduce the risk of missed doses.
- Home medication delivery services for older adults with mobility or transportation challenges.
- Comprehensive medication therapy management consultations to optimize drug therapy and address medication-related concerns.
Advancements in Pharmacy Practice for Aging Populations
- Technological innovations such as automated medication dispensing systems and electronic prescribing platforms enhance medication safety and convenience for elderly patients.
- Pharmacogenomic testing allows pharmacists to personalize drug therapy based on an individual’s genetic makeup, reducing the risk of adverse reactions and improving treatment outcomes.
- Collaborative practice agreements enable pharmacists to provide direct patient care services, including medication management and chronic disease management, in partnership with other healthcare providers.
Weight Loss
Weight management is crucial for the elderly as it can have a significant impact on their overall health and well-being. As we age, our metabolism slows down, making it harder to lose weight and easier to gain it. However, maintaining a healthy weight is essential for preventing chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.
Implications of Weight Management in the Elderly
- Excess weight can exacerbate existing health issues and increase the risk of developing new ones.
- Carrying extra weight can put additional strain on joints, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
- Being overweight or obese can contribute to feelings of fatigue and decrease quality of life.
Challenges Faced by Aging Individuals in Losing Weight
- Slower metabolism can make it more difficult to burn calories.
- Age-related muscle loss can decrease overall energy expenditure.
- Medical conditions and medications can impact weight loss efforts.
Tips for Healthy Weight Loss Strategies for Older Adults
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Aim for regular physical activity, including both aerobic and strength training exercises.
- Stay hydrated and monitor portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist for personalized guidance and support.
Importance of Balanced Diet and Exercise in Weight Management for the Elderly
- A balanced diet provides essential nutrients for overall health and helps maintain muscle mass.
- Regular exercise can improve metabolism, increase energy levels, and enhance physical function.
- Combining healthy eating habits with physical activity can lead to sustainable weight loss and better quality of life.
Women & Health
Women have unique healthcare needs as they age, requiring specialized attention and care to maintain their well-being. Elderly women often face specific health issues that may differ from those of men, necessitating targeted preventive measures and healthcare services.
Unique Healthcare Needs of Aging Women
- Elderly women are more likely to experience conditions such as osteoporosis, urinary incontinence, and heart disease due to hormonal changes and aging.
- Regular screenings for breast and cervical cancer are crucial for early detection and treatment in older women.
- Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are common among aging women and require proper diagnosis and management.
Common Health Issues Faced by Elderly Women
- Osteoporosis: Women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis as they age, leading to fragile bones and an increased susceptibility to fractures.
- Urinary Incontinence: Bladder control problems are prevalent in elderly women, impacting their quality of life and requiring specialized treatment options.
- Heart Disease: Cardiovascular health is a significant concern for aging women, necessitating lifestyle modifications and preventive measures to reduce the risk of heart-related issues.
Preventive Healthcare Measures Specific to Women in Older Age
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help prevent osteoporosis and improve bone health in elderly women.
- Regular physical activity, such as strength training and aerobic exercises, can enhance cardiovascular fitness and overall well-being in aging women.
- Annual screenings for breast cancer and Pap smears are essential for early detection of potential health concerns in older women.
Specialized Healthcare Services for Aging Women
- Geriatric care programs tailored to the specific needs of elderly women, including comprehensive health assessments and personalized treatment plans.
- Menopause clinics offering specialized services and support for women navigating hormonal changes and related health issues in older age.
- Women’s health centers providing a range of services, from preventive screenings to menopausal management, to address the unique healthcare needs of aging women.
Summary
As we conclude our exploration of healthcare for aging populations, it becomes evident that the intersection of specialized programs and technological innovations holds the key to ensuring a healthier and more fulfilling life for the elderly. With a focus on tailored care and cutting-edge solutions, the future of healthcare for aging populations looks brighter than ever.
FAQ Guide
What are some common health issues faced by aging populations?
Common health issues include arthritis, hypertension, diabetes, and cognitive decline.
How does technology impact healthcare for aging populations?
Technology improves access to medical information, enables remote monitoring, and enhances communication between healthcare providers and elderly patients.
What are some examples of successful addiction treatment programs for the elderly?
Programs like individual counseling, group therapy, and medication-assisted treatment have shown positive outcomes in addressing addiction in aging populations.